基因沉默指令通过染色质上的‘分子记忆’标签获取
来源:《Molecular Cell》
作者:Todd Blevins等
时间:2014-04-08
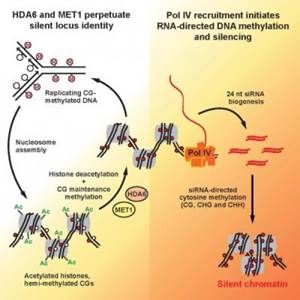
表观遗传是一个两步程序,首先形成可遗传的分子记忆维持染色质状态,该状态是后期基因位点实际沉默所必须的。
印第安那大学的科学家已经解开了一个现代遗传学之密:获得的性状如何通过称为表观遗传这一过程在几代之间传递。新的研究发现,细胞不能使基于DNA序列编码信息的一些基因沉默,但能识别添加到基因的可遗传化学标记。这些化学标签以一种分子记忆的形式,使细胞识别基因,并记住使其在新的每一代沉默。
由生物学家和生物化学家Craig Pikaard 带领的印第安那大学的科学家队伍有12个成员,他们的发现为深入洞察植物细胞如何判断并使遗传位点沉默提供了重要的新渠道。
代替依靠内在基于DNA序列的信息,细胞必须依靠烙印在DNA和蛋白质组成的复合物染色质上的化学标记来唤醒使特定基因位点沉默记忆。此外,去除一个碳(甲基)或两个碳(乙酰)化学标记也是修饰染色质的方式,从而赋予基因位点除DNA编码信息以外的表观遗传信息。
维持染色质标记作为一种表观遗传记忆的形式的能力,即Pikaard所说的赋予沉默位点识别的预先建立状态的能力,是细胞所需要的,用来向位点传达完成称为RNA指导的DNA甲基化沉默(RdDM)的机制。RdDM过程涉及短干扰RNA(siRNA),它由24个核苷酸组成的小RNA分子,引导甲基群与DNA链匹配结合,最终使基因沉默失活。(编译:中国科学院成都生物研究所 王芋华,王海燕)
A two-step process for epigenetic inheritance in Arabidopsis
Abstract In Arabidopsis, multisubunit RNA polymerases IV and V orchestrate RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM) and transcriptional silencing, but what identifies the loci to be silenced is unclear. We show that heritable silent locus identity at a specific subset of RdDM targets requires HISTONE DEACETYLASE 6 (HDA6) acting upstream of Pol IV recruitment and siRNA biogenesis. At these loci, epigenetic memory conferring silent locus identity is erased in hda6 mutants such that restoration of HDA6 activity cannot restore siRNA biogenesis or silencing. Silent locus identity is similarly lost in mutants for the cytosine maintenance methyltransferase, MET1. By contrast, pol IV or pol V mutants disrupt silencing without erasing silent locus identity, allowing restoration of Pol IV or Pol V function to restore silencing. Collectively, these observations indicate that silent locus specification and silencing are separable steps that together account for epigenetic inheritance of the silenced state.
原文链接:http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1097276514001646




