科学家开发出生物质燃料低温电池
来源:《Nature Communications》
作者:Liu Wei等
时间:2014-03-27

借助太阳能或废热就能将稻草、藻类等转化为电能
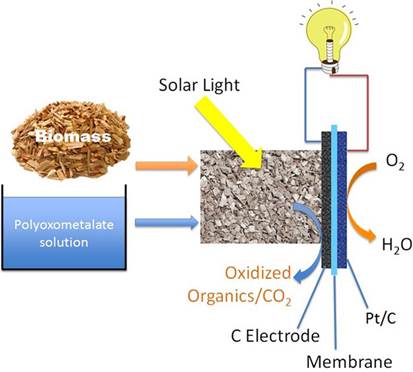
前聚合物交换膜燃料电池技术不能直接使用生物质作为燃料。日前,美国和中国科学家开发出一种直接以生物质为原料的低温燃料电池。
这是一种太阳能诱导混合燃料电池,直接采用淀粉、纤维素、木质素甚至柳枝稷和木粉等天然生物质提供动力。电池利用多金属氧酸盐为催化剂和载荷体进行低温发电。这类太阳能诱导混合燃料电池结合了太阳能电池、燃料电池和氧化还原液流电池的特点。太阳能诱导的混合燃料电池的纤维素供电功率密度达到mW cm−2,几乎是纤维素微生物燃料电池的100倍,与文献报道的最好的微生物燃料电池相当。不同于大多数电池对杂质敏感,这类太阳能诱导混合燃料电池对燃料中大多数有机和无机污染物表现惰性。(编译:中国科学院成都生物研究所 王芋华,王海燕)
Solar-induced direct biomass-to-electricity hybrid fuel cell using polyoxometalates as photocatalyst and charge carrier
Abstract The current polymer-exchange membrane fuel cell technology cannot directly use biomass as fuel. Here we present a solar-induced hybrid fuel cell that is directly powered with natural polymeric biomasses, such as starch, cellulose, lignin, and even switchgrass and wood powders. The fuel cell uses polyoxometalates as the photocatalyst and charge carrier to generate electricity at low temperature. This solar-induced hybrid fuel cell combines some features of solar cells, fuel cells and redox flow batteries. The power density of the solar-induced hybrid fuel cell powered by cellulose reaches 0.72 mW cm−2, which is almost 100 times higher than cellulose-based microbial fuel cells and is close to that of the best microbial fuel cells reported in literature. Unlike most cell technologies that are sensitive to impurities, the cell reported in this study is inert to most organic and inorganic contaminants present in the fuels.
原文链接:http://www.nature.com/ncomms/2014/140207/ncomms4208/full/ncomms4208.html




