
中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院合肥智能机械研究所黄行九团队利用分级多孔铈锆双金属氧化物纳米材料,对不同重金属离子吸附速率的差异实现了微污染物Pb(II)的高灵敏度、高选择性检测。
在当前的重金属离子的检测中,电化学方法已得到广泛应用。但由于利用溶出伏安法检测重金属离子(如Cu(II)、 Hg(II)、 Pb(II)、Cd(II)、Zn(II))时,不同的重金属离子之间能形成金属间的化合物,在富集过程中在修饰的电极表面的吸附产生竞争,从而使得同时检测多种重金属离子时产生较为严重的干扰,无法准确地检测某种特定重金属离子。因此,寻找能够实现选择性及准确检测某种特定重金属离子的方法成为需求。
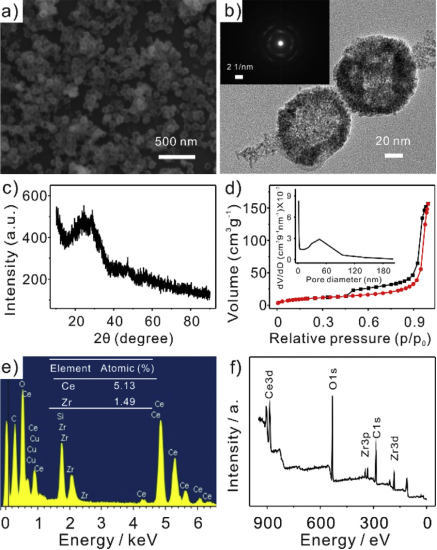
黄行九团队利用分级多孔铈锆双金属氧化物纳米球(Ce-Zr)作为电极材料,借助其对重金属离子的吸附作用,详细研究了Ce-Zr氧化物纳米球构筑的电化学敏感界面对重金属离子检测的阳极溶出伏安行为。研究结果表明,分析方法能够实现对Pb(II)的高灵敏、高选择性及高抗干扰检测。同时,研究人员结合X-射线光电子能谱(XPS)技术及大量的吸附实验,详细深入地研究了Ce-Zr氧化物纳米球选择性检测Pb(II)的可能机理。研究结果表明,不同重金属离子在Ce-Zr氧化物纳米球表面吸附的速率有很大差异,在吸附很短的一段时间内(< 150 s),Ce-Zr氧化物纳米球对Pb(II)的吸附量远大于其他几种离子,而由于电化学检测富集时间比较短,电极材料表面吸附目标物质的量决定电化学溶出信号的高低,在溶出伏安分析的富集阶段吸附更多的Pb(II),从而还原沉积更多的Pb(0)到电极表面,进而在溶出过程中获得增强的电化学信号。因此,Ce-Zr氧化物纳米球构筑的电化学敏感界面能够实现对Pb(II)的高灵敏及高选择性检测。黄行九团队利用以上方法对合肥望塘污水处理厂进水口水样中的Pb(II)进行检测,获得了准确的检测结果与满意的回收率,表明该分析方法具有检测实际水样中污染物Pb(II)的应用潜力。
相关研究成果已发表在Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical上。该研究得到了国家自然科学基金、中科院创新交叉团队、合肥研究院院长基金等的资助。(来源:中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院)
Sensitive and interference-free electrochemical determination of Pb(II) in wastewater using porous Ce-Zr oxide nanospheres
Abstract Herein, combined the synergetic effects and excellent adsorption of binary oxides, a novel sensor interface was designed by using porous Ce-Zr oxide nanospheres modified glassy carbon electrode (Ce-Zr oxide/GCE), which has successfully realized high sensitivity and anti-interference detection of Pb(II). The electrochemical determination of Pb(II) has been investigated by square wave anodic stripping voltammetry (SWASV) range from 0.02 to 0.5 μM, and a high sensitivity per unit area of 1666.02 μA μM−1 cm−2 was obtained with a limit of detection of 0.006 μM (3σ method). The enhancement of Pb(II) stripping signal is attributed to the excellent adsorption performance of porous Ce-Zr oxide nanospheres, which has been confirmed with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Importantly, Ce-Zr oxide/GCE possesses highly anti-interference ability against the influence of Hg(II), Cd(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) in the determination of Pb(II). Meanwhile, the remarkable stability and reproducibility were obtained. Finally, the accurate analysis of Pb(II) in wastewater collected from Wangtang sewage disposal plant was achieved. These results indicate that porous Ce-Zr oxide nanospheres are identified as promising modifier for the reliable and accurate determination of Pb(II).
原文链接:https://ac.els-cdn.com/S0925400517321925/1-s2.0-S0925400517321925-main.pdf?_tid=cb397f06-d313-11e7-9c95-00000aab0f6c&acdnat=1511746942_0fc71665781d93ba11b0d964921b983a



