
北京林业大学张德强团队在对杨树不同类型群体进行大规模表型与分子数据测定和统计分析的基础上,在全球范围内率先完成了林木数量性状“连锁—连锁不平衡联合作图”研究。相关成果日前在线发表于《新植物学家》杂志。
对生长周期长、遗传背景复杂、研究基础薄弱的林木而言,如何利用模式树种基因组信息,建立系统的数量性状解析新策略,构建高效的分子设计育种理论,从而加速林木遗传改良进程,一直是林木分子育种研究的最前沿与关注的热点。
此次研究人员以1200株杨树家系群体为材料,构建了包含19个连锁群、1274个标记的高密度、高析度遗传连锁图谱,覆盖杨树基因组长度约96.9%,并对参与木材形成的314个关键基因进行了精细定位。
此项成果受到林木分子育种领域多位权威专家的关注。美国农业部森林研究所主任、《新植物学家》副主编Andrew Groover表示:“该实验设计的系统性与数据量的丰富性令人赞叹。利用联合作图策略解析林木生长性状遗传结构的研究,将给从事林木分子基础研究的科学家提供重要的学术思路和研究手段。”
美国科学院院士、国际著名林木遗传学家Ronald Sederoff评价说:“该研究的深度值得称赞,展示了令人难以置信的数据量和分析水平。”(来源:中国科学报 郑金武 铁铮 杨丽娜)
Genetic architecture of growth traits in Populus revealed by integrated quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis and association studies
Abstract Deciphering the genetic architecture underlying polygenic traits in perennial species can inform molecular marker-assisted breeding. Recent advances in high-throughput sequencing have enabled strategies that integrate linkage–linkage disequilibrium (LD) mapping in Populus.
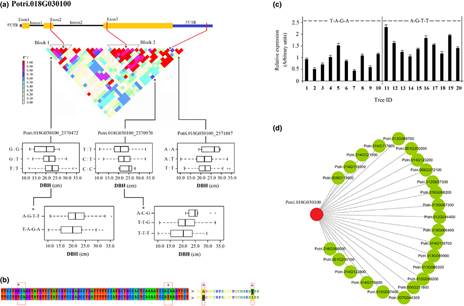
We used an integrated method of quantitative trait locus (QTL) dissection with a high-resolution linkage map and multi-gene association mapping to decipher the nature of genetic architecture (additive, dominant, and epistatic effects) of potential QTLs for growth traits in a Populus linkage population (1200 progeny) and a natural population (435 individuals).
Seventeen QTLs for tree height, diameter at breast height, and stem volume mapped to 11 linkage groups (logarithm of odds (LOD) ≥ 2.5), and explained 2.7–18.5% of the phenotypic variance. After comparative mapping and transcriptome analysis, 187 expressed genes (10 046 common single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)) were selected from the segmental homology regions (SHRs) of 13 QTLs. Using multi-gene association models, we observed 202 significant SNPs in 63 promising genes from 10 QTLs (P ≤ 0.0001; FDR ≤ 0.10) that exhibited reproducible associations with additive/dominant effects, and further determined 11 top-ranked genes tightly linked to the QTLs. Epistasis analysis uncovered a uniquely interconnected gene–gene network for each trait.
This study opens up opportunities to uncover the causal networks of interacting genes in plants using an integrated linkage–LD mapping approach.
原文链接:http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/nph.13695/full;jsessionid=1C4E509435764C70864CF3B6398598F2.f02t04?wol1URL=/doi/10.1111/nph.13695/full®ionCode=CN-AH&identityKey=3aa75a7b-7fe7-4e89-bcb1-beaed490c8d6



